5.1 KiB
| title | published | description | tags | cover_image | canonical_url | id |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #90DaysOfDevOps - Let's explain the Hello World code - Day 9 | false | 90DaysOfDevOps - Let's explain the Hello World code | devops, 90daysofdevops, learning | null | null | 1048732 |
讓我們解釋一下 Hello World 編碼
GO程式語言如何運作
在第 8 天,我們瀏覽了您在工作站上安裝 Go 的過程,然後我們創建了我們第一個 Go的應用程序。
在本章節中,我們將更深入地研究代碼並了解更多關於 Go 程式語言的內容。
什麼是編譯?
在我們進入第6行Hello World代碼之前,6 lines of the Hello World code 我們必需要對編譯有一點了解。
像我們常用的Python, Java, Go and C++編程語言都是高階的程試語言。 這意味著它們是人類可辨別的,但是當機器嘗試執行程序時,它需要採用機器可以理解的形式。我們必須將人類可辨別的代碼翻譯成為機器代碼這就稱為編譯。
From the above you can see what we did on Day 8 here, we created a simple Hello World main.go and we then used the command go build main.go to compile our executable.
What are packages?
A package is a collection of source files in the same directory that are compiled together. We can simplify this further, a package is a bunch of .go files in the same directory. Remember our Hello folder from Day 8? If and when you get into more complex Go programs you might find that you have folder1 folder2 and folder3 containing different .go files that make up your program with multiple packages.
We use packages so we can reuse other peoples code, we don't have to write everything from scratch. Maybe we are wanting a calculator as part of our program, you could probably find an existing Go Package that contains the mathematical functions that you could import into your code saving you a lot of time and effort in the long run.
Go encourages you to organise your code in packages so that it is easy to reuse and maintain source code.
Hello #90DaysOfDevOps Line by Line
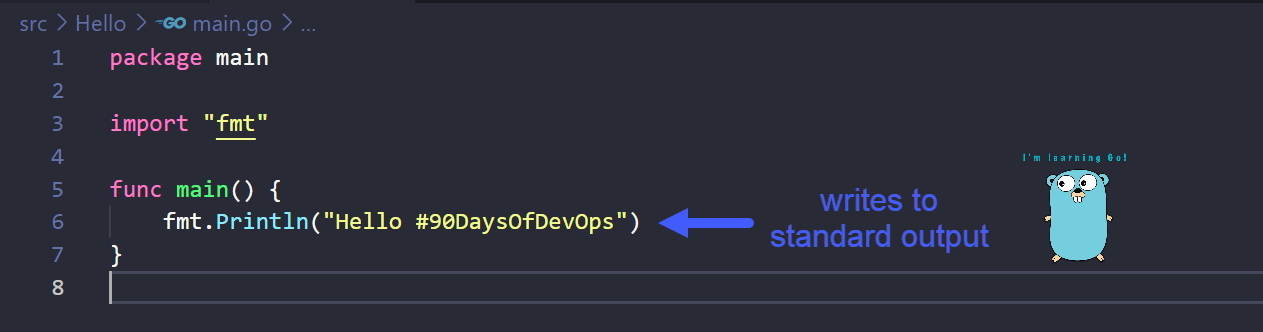
Now let's take a look at our Hello #90DaysOfDevOps main.go file and walk through the lines.
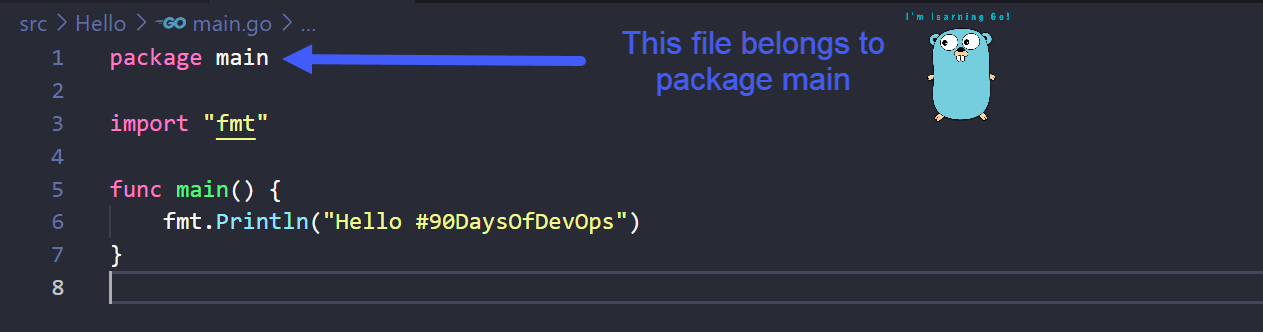
In the first line, you have package main which means that this file belongs to a package called main. All .go files need to belong to a package, they should also have package something in the opening line.
A package can be named whatever you wish. We have to call this main as this is the starting point of the program that is going to be in this package, this is a rule. (I need to understand more about this rule?)
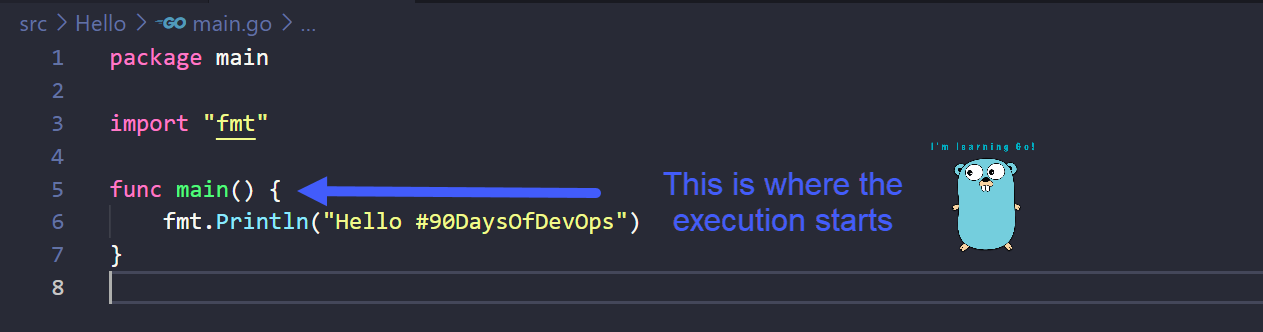
Whenever we want to compile and execute our code we have to tell the machine where the execution needs to start. We do this by writing a function called main. The machine will look for a function called main to find the entry point of the program.
A function is a block of code that can do some specific task for and can be used across the program.
You can declare a function with any name using func but in this case we need to name it main as this is where the code starts.
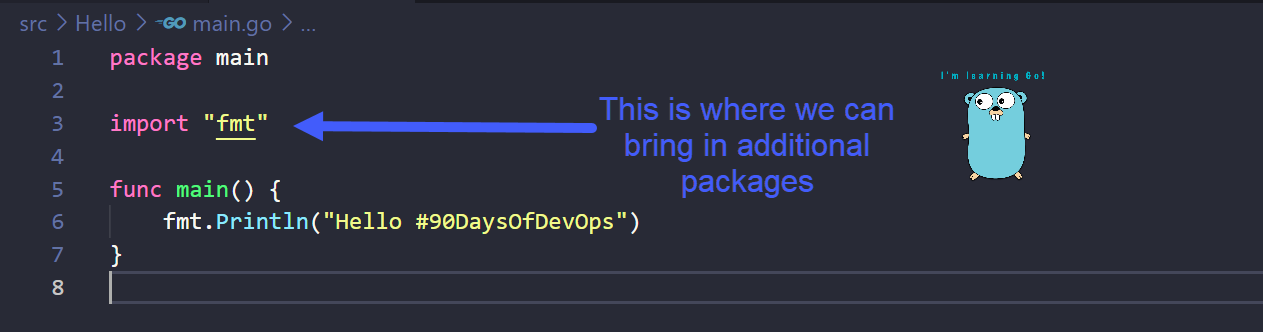
Next we are going to look at line 3 of our code, the import, this basically means you want to bring in another package to your main program. fmt is a standard package being used here provided by Go, this package contains the Println()function and because we have imported this we can use this in line 6. There are a number of standard packages you can include in your program and leverage or reuse them in your code saving you the hassle of having to write from scratch. Go Standard Library
the Println() that we have here is a way in which to write to a standard output to the terminal where ever the executuable has been executed succesfully. Feel free to change the message in between the ().
TLDR
- Line 1 = This file will be in the package called
mainand this needs to be calledmainbecause includes the entry point of the program. - Line 3 = For us to use the
Println()we have to import the fmt package to use this on line 6. - Line 5 = The actual starting point, its the
mainfunction. - Line 6 = This will let us print "Hello #90DaysOfDevOps" on our system.
Resources
- StackOverflow 2021 Developer Survey
- Why we are choosing Golang to learn
- Jake Wright - Learn Go in 12 minutes
- Techworld with Nana - Golang full course - 3 hours 24 mins
- NOT FREE Nigel Poulton Pluralsight - Go Fundamentals - 3 hours 26 mins
- FreeCodeCamp - Learn Go Programming - Golang Tutorial for Beginners
- Hitesh Choudhary - Complete playlist
See you on Day 10.